What makes the Earth interesting?
In contrast to different planets of our nearby planetary group, life formed into numerous structures on the Earth after its rise. Fluid water and oxygen for breathing made this conceivable. A huge number of types of plants and creatures flourish today ashore and in water. Water covers more than 66% of the Earth's surface. Subsequently, the Earth seems blue from the moon or from the International Space Station. Therefore, it is additionally called the 'blue planet. Till now, researchers have not found life in some other spot in the universe, however they accept that one day they will do as such.
How was the Earth shaped?
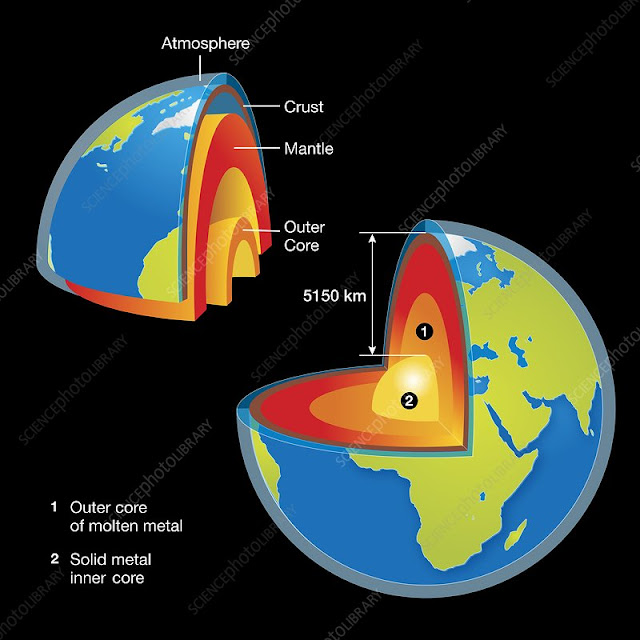
The Earth, alongside the sun and the leftover planets of our close planetary system, started around 4.8 billion years prior from dust particles, which agglomerated steadily. Around then, the youthful Earth was besieged by innumerable shooting stars from space. The Earth's inside was liquid and volcanoes emitted continually. Yet, more than a long period of time, the Earth's surface chilled off. Around 3.8 billion years prior, the temperature diminished to about 100'C and the Earth's outside gradually began getting strong. As of now the vaporous cover on the Earth was generally comprised of water fume.
For what reason did life create on the Earth?
The starting point of life on the Earth is a blessed arrangement of occasions. The Earth's separation from the sun was with the end goal that its air and surface chilled off to a moderate level. Fluid water-and not simply water fume additionally framed, and it didn't freeze as the sun was not very far away. The cooling of the Earth offered ascend to a sort of 'early stage sea'. The activity of the UV beams of the sun, the lightning streaks created by storms, and the innumerable volcanic ejections offered ascend to new complex synthetic mixtures. Around 4 billion years prior, the main particles showed up, from whích the principal unicellular creatures were framed.
Where does the oxygen we inhale come from?
Vaporous oxygen was made on the Earth about 3.5 billion years prior. Around then, the UV light of the sun deteriorated the water fume atoms present in the air, and delivered oxygen and hydrogen. However, a significant piece of the oxygen quickly responded with different substances, so it was not, at this point accessible in the environment as gas. Oxygen was likewise created by the oceans, where the 'blue green growth' did photosynthesis. These microbes changed over daylight and carbon dioxide into energy. Simultaneously, vaporous oxygen was delivered as a 'byproduct', which amassed in the environment. Around one billion years prior, around one-20th (4%) of the air comprised of oxygen.
What might occur if there was no water on the Earth?
Without water, there would be no creatures or plants, which do photosynthesis and delivery oxygen, and therefore the oxygen content in the air would go down. Besides, the shortfall of seas would have genuine results as they help to keep the Earth's environment moderate by putting away warmth inside them. Without huge water bodies, the temperatures of the sunlit and those away from the daylight would change radically. The temperature contrast between day There is no life on different planets and night and among summer and winter would be exceptionally enormous. Therefore, tropical storms would be a steady event on the Earth.
Is there life on any planet other than the Earth?
There is no life on different planets in our close planetary system in light of the fact that their surroundings are not great forever. They are either excessively hot, excessively cold, or excessively turbulent. The solitary consistent event on the Earth. place that can be expected fit for supporting life is Europa, the moon of Jupiter. Researchers say that an expanse of fluid water could be available on this divine body under a 10-km thick layer of ice. They likewise say that human advancements like our own could be available if by any stretch of the imagination just outside of our nearby planetary group.



Comments
Post a Comment